Related Divisions
Carnegie's newest scientific division, Biosphere Sciences & Engineering, is devoted to disrupting the traditional, siloed perspective on research in the life sciences and pursuing an integrated approach to solving humanity's greatest challenges.
Biosphere Sciences & EngineeringDrawing on more than a century of science, our multidisciplinary department discovers exoplanets, creates new materials, illuminates Earth's inner workings, and seeks to better understand the universe that is our home.
Earth & Planets LaboratoryRelated News
On ice giant planets, diamond forms at shallower depths than previously thought. Because it is denser than the surrounding material, it sinks deeper—a phenomenon sometimes called “diamond rain”—providing an additional heat source, which could drive convection in the ice layer and contribute to these planets’ complex magnetic fields.
“I could have stuck to working with cyanobacteria and been content,” Bhaya said. “But this overwhelming richness of information was just too much to pass up. ... The ‘omics approach has changed how people think about sharing their data and about biology as a more communal field of research."
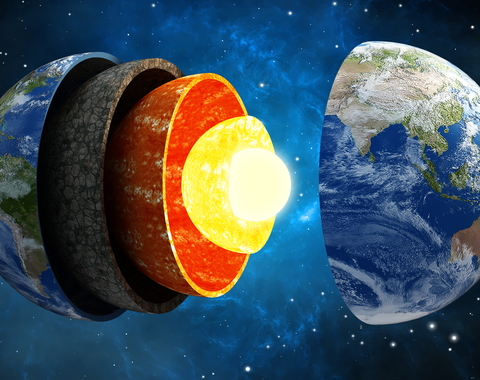
The mantle is predominately silicate, but its concentrations of so-called “iron-loving,” or siderophile, elements have mystified scientists for decades.
Tissint, which crash landed in Morocco more than 11 years ago, is one of only five Martian meteorites that have been observed as they fell to Earth.