Financials
The Carnegie Institution for Science completed fiscal year 2020 in sound financial condition after generating a net return of 2.1% on the diversified investments within its endowment; maintaining a disciplined spending policy that balances today’s needs with the long-term requirements of the institution and the interests of future scientists; and the continued support of organizations and individuals who recognize the value of basic science.
The primary source of support for the institution’s activities continues to be its endowment. This reliance on institutional funding provides an important degree of independence in the research activities of the institution’s scientists.
As of June 30, 2020, the endowment was valued at $927 million. Over the period 1998-2020, average annual distributions from the endowment to the budget were 5.0%. Carnegie closely controls expenses to ensure the continuation of a healthy scientific enterprise.
For several years, under the direction of the Investment Committee of the Board, Carnegie’s endowment has been allocated among a broad spectrum of asset classes including: global equities, absolute return investments, real estate partnerships, private equity, venture capital, natural resources partnerships, and government bonds. The goal of this diversified approach is to generate attractive overall performance and reduce the volatility that would exist in a less diversified portfolio. In 2016 Carnegie hired its first Chief Investment Officer to more proactively steward the endowment’s assets.
The Chief Investment Officer and Investment Committee regularly examine the asset allocation of the endowment and readjust the allocation, as appropriate. The institution relies upon external managers and partnerships to conduct the investment activities, and it employs a commercial bank to maintain custody. The following chart shows the allocation of the institution’s endowment among asset classes as of June 30, 2020.
| Asset Class | Target | Actual |
|---|---|---|
| Common Stock | 41.0% | 39.1% |
| Alternative Assets | 47.0% | 53.1% |
| Fixed Income and Cash | 12.0% | 7.8% |
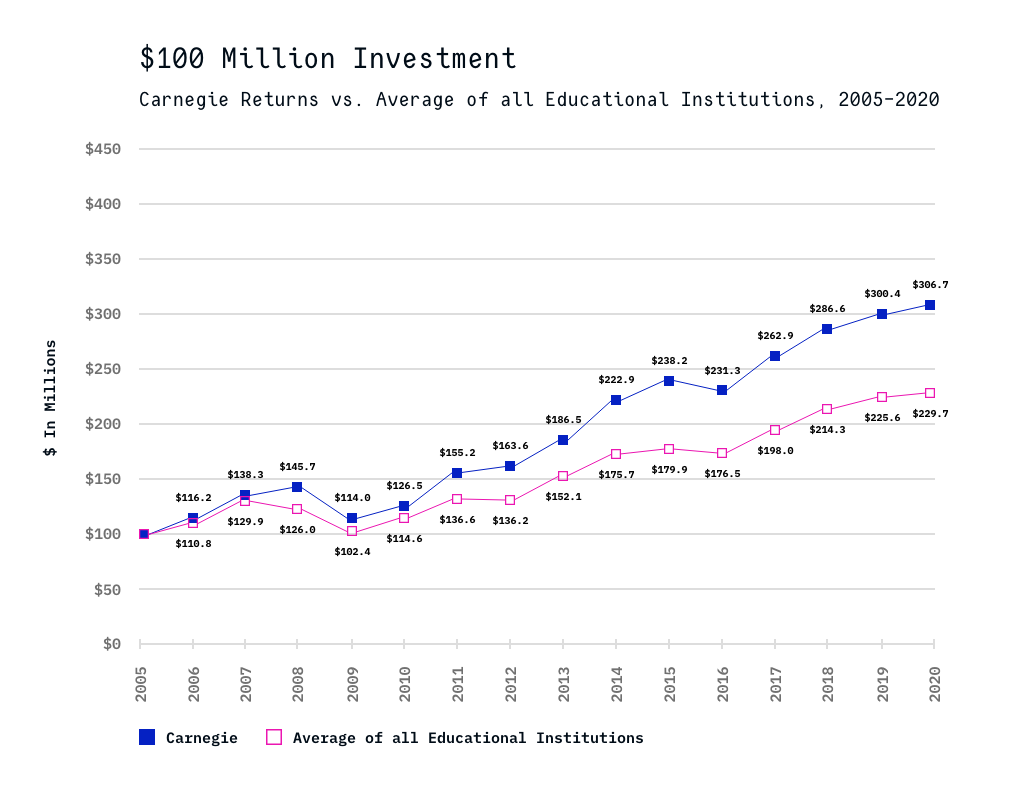
Carnegie’s investment goals are to provide high levels of current support to the institution and to maintain the long-term spending power of its endowment. The success of Carnegie’s investment strategy is illustrated in the following figure that compares, for a hypothetical investment of $100 million, Carnegie’s investment returns with the average returns for all educational institutions for the last fifteen years.
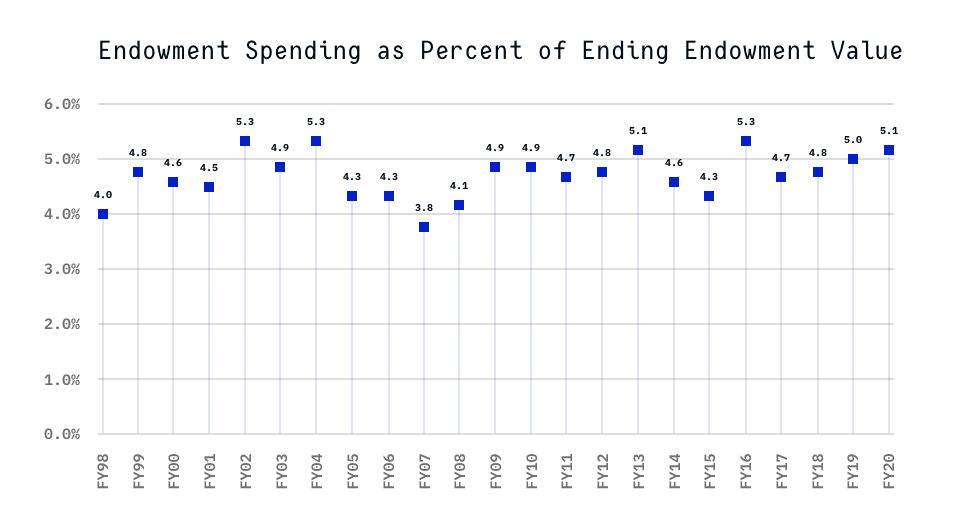
Carnegie has pursued a long-term policy of controlling its spending rate by using a hybrid spending rate, which in the long term contributes 5% of the endowment for annual use. Carnegie employs what is known as a 70/30 hybrid spending rule. That is, the amount available from the endowment in any year is made up of 70% of the previous year’s budget, adjusted for inflation, and 30% of the most recently completed year-end endowment value, multiplied by the spending rate of 5% and adjusted for inflation and debt. This method reduces volatility from year-to-year. The following figure depicts actual spending as a percentage of ending market value for the last 20 years.
In fiscal year 2020, Carnegie benefitted from continuing federal support. Carnegie received $16.5 million in new/additional federal grants in 2020. This is a testament to the high quality of Carnegie scientists and their ability to compete successfully for federal funds.
Within Carnegie’s endowment, there are several “funds” that provide support either in a general way or targeted to a specific purpose. The largest of these is the Andrew Carnegie Fund, begun with the original gift of $10 million. Mr. Carnegie later made additional gifts totaling another $12 million during his lifetime. This tradition of generous support for Carnegie’s scientific mission has continued throughout our history and a list of donors in fiscal year 2020 appears in an earlier section of this Year Book. In addition, Carnegie receives important private grants for specific research purposes.
Carnegie Institution of Washington
Statement of Financial Position
July 30, 2020 and 2019
(in thousands)
| Assets | 2020 | 2019 |
| Cash and Cash Equivalents | 30,125 | 33,050 |
| Contributions Receivable | 3,728 | 3,750 |
| Accounts Receivable and other assets (net) | 9,265 | 7,743 |
| Bond Proceeds | 120,582 | 21,661 |
| Investments | 917,741 | 953,113 |
| Property and equipment (net) | 118,276 | 126,641 |
| Long term deferred asset | 61,596 | 60,460 |
| Total assets | 1,261,313 | 1,206,418 |
| Liabilities | ||
| Accounts payable and accrued expenses | 11,403 | 12,069 |
| Deferred revenue | 28,587 | 26,828 |
| Bonds payable | 214,348 | 115,032 |
| Accrued Postretirement benefits | 32,741 | 27,721 |
| Total liabilities | 287,079 | 181,650 |
| Net Assets | ||
| Without donor restriction | 295,115 | 311,622 |
| With donor restriction | 679,119 | 713,146 |
| Total net assets | 1,024,768 | |
| Total liabilities and net assets | 1,261,313 | 1,206,418 |
Carnegie Institution of Washington
Statement of Activities
July 30, 2020 and 2019
(in thousands)
| Revenue and Support | 2020 | 2019 |
| Grants and contracts | 17,668 | 20,526 |
| Contributions, gifts | 4,493 | 7,987 |
| Other Income | 2,358 | 7,559 |
| Net external Revenue | 24,519 | 36,072 |
| Investment income and unrealized gains | 17,816 | 31,221 |
| Total Revenue | 42,335 | 67,293 |
| Expenses | ||
| Program and Supporting Services: | ||
| Terrestrial Magnetism | 10,274 | 10,039 |
| Observatories | 24,078 | 23,055 |
| Geophysical Laboratory | 11,809 | 13,294 |
| Embryology | 13,471 | 14,697 |
| Plant Biology | 9,173 | 9,360 |
| Global Ecology | 4,792 | 7,123 |
| Other Programs | 278 | 1,013 |
| Administration and general expenses | 14,416 | 14,968 |
| Total Expenses | 88,291 | 93,549 |
| Change in net assets before pension related changes | (45,956) | (25,378) |
| Pension related changes | (3,649) | (2,611) |
| Other components of postretirement benefit expense | (929) | (878) |
| Grant modifications | (5,188) | |
| Net Assets at the beginning of the period | 1,024,768 | 1,058,823 |
| Net assets at the end of the period | 974,234 | 1,024,768 |
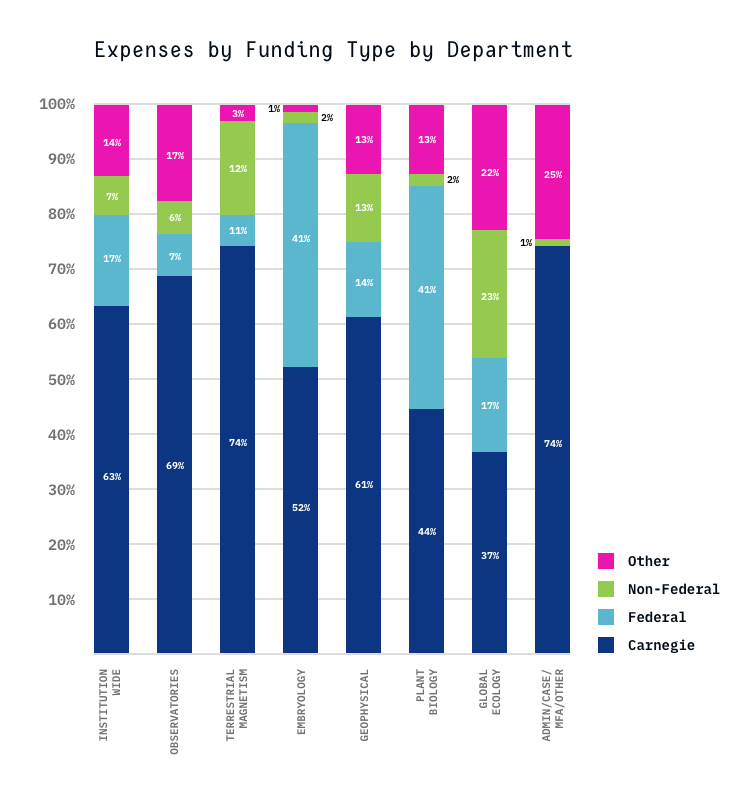
READER’S NOTE: In this section, we present summary financial information. Each year the Carnegie Institution, through the Audit Committee of its Board of Trustees, engages an independent auditor to express an opinion about the financial statements and the financial position of the institution. The complete audited financial statements are made available on the institution’s website.
